
- Split plot one way anova examples by hand how to#
- Split plot one way anova examples by hand software#
Since this p-value is not less than 0.05, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. To perform a one-way ANOVA on this data, we will use the Statology One-Way ANOVA Calculator with the following input:įrom the output table we see that the F test statistic is 2.358 and the corresponding p-value is 0.11385. The exam scores for each group are shown below: At the end of the three weeks, all of the students take the same exam. The students in each group are randomly assigned to use one of the three exam prep programs for the next three weeks to prepare for an exam. To test this, we recruit 30 students to participate in a study and split them into three groups. Suppose we want to know whether or not three different exam prep programs lead to different mean scores on a certain exam. To determine this, you need to perform post hoc tests, also known as “multiple comparisons” tests. Note: If you reject the null hypothesis, this indicates that at least one of the population means is different from the others, but the ANOVA table doesn’t specify which population means are different. 0.05), then you can reject the null hypothesis and conclude that at least one of the population means is different from the others. If the p-value is less than your chosen significance level (e.g.
Split plot one way anova examples by hand software#
No matter which software you use, you will receive the following table as output: Source You will typically use some statistical software (such as R, Excel, Stata, SPSS, etc.) to perform a one-way ANOVA since it’s cumbersome to perform by hand.
Split plot one way anova examples by hand how to#
Read this article for in-depth details on how to check these assumptions. Independence – The observations in each group are independent of each other and the observations within groups were obtained by a random sample. You can use Bartlett’s Test to verify this assumption.ģ. Equal Variances – The variances of the populations that the samples come from are equal. Normality – Each sample was drawn from a normally distributed population.Ģ. One-Way ANOVA: Assumptionsįor the results of a one-way ANOVA to be valid, the following assumptions should be met:ġ. Fortunately, a one-way ANOVA allows us to answer this question. The question is whether or not this difference is statistically significant.
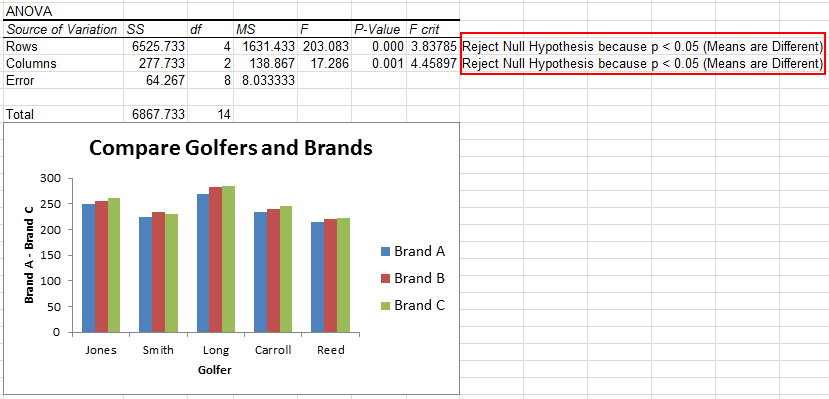
However, it’s virtually guaranteed that the mean exam score between the three samples will be at least a little different. Then, we could record the scores for each student once they take the exam. Instead, we might select three random samples of 100 students from the population and allow each sample to use one of the three test prep programs to prepare for the exam. Since there are millions of high school students around the country, it would be too time-consuming and costly to go around to each student and let them use one of the exam prep programs. Suppose we want to know whether or not three different exam prep programs lead to different mean scores on a college entrance exam. An example of how to perform a one-way ANOVA.The process to perform a one-way ANOVA.The assumptions that should be met to perform a one-way ANOVA.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
